Geography of Ukraine
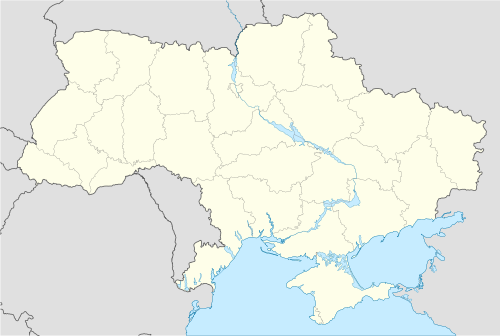

Ukraine is the second-largest country in Europe. Its geography varies significantly depending on regions.
Contents |
Geographic location
Ukraine has a strategic position in Eastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea in the south, Poland, Slovakia and Hungary in the west, Belarus in the north, Moldova and Romania in the south-west and Russia in the east.
The northern part of the Carpathian Mountains (highest peak Hoverla, 2061 m or 6762 ft) reaches into Ukraine in the western part of the country, but most of its area is taken up by the steppe-like region just north of the Black Sea. Ukraine is divided almost in half by the Dnipro river, which traverses Ukraine north to south. It is joined by the Black Sea, which is west of the Crimea and near the mouths of the Bug and the Dnister rivers. The border with Russia is the longest and runs through the Sea of Azov.
Land
The total geographic area of Ukraine is 603,700 square kilometers (233,100 sq mi). The land border of Ukraine is, in total, 4,558 kilometers (2,832 mi). It is bordered by Belarus (891 km), Hungary (103 km), Moldova (939 km), Poland (428 km), Romania (169 km on the south, 362 km on the west), Russia (1576 km) and Slovakia (90 km). Ukraine is also bordered by 3,783 kilometers (2,351 mi) of coastline.
Most of Ukraine consists of fertile plains (steppes) and plateaus, mountains being found only in the west (the Carpathians), in the Crimean Peninsula in the extreme south (the Crimean Mountains), and some eroded one in the east closer to the Sea of Azov (the Donets Ridge). The highest elevation in Ukraine is recorded at the Mount Hoverla, at 2,061 meters (6,762 ft). In terms of land use, 58% of Ukraine is considered arable land; 2% is used for permanent crops, 13% for permanent pastures, 18% is forests and woodland and 9% is other.
Relief
The larger part of Ukraine consists of regular plains with the average height above sea level being 175 m (550 feet). It is surrounded by mountains to its west and extreme south. Wide spaces of the country's plains that constitute the south-western part of the East European Plain for its relief are not all the same. One may outline numerous highlands and lowlands establishment of which is caused mostly by the uneven crystallized base of the East European craton. Highlands mainly are associated with the Ukrainian Shield.
Ukraine has some other highlands as well as its mountains amongst which are the Volyn-Podillia Upland (in the west), the Near Dnipro Upland (the right bank of Dnipro), to the east there are the south-western spurs of the Central Russian Upland upon which runs the border with Russia, the Donets Ridge and the Near Azov Upland closer to the Sea of Azov.
The major lowlands are the Polissian Lowland (in the north), the Black Sea Coastal Lowland (in the south) and the Dnipro River Lowland that is located in the north on the left bank of Dnipro river.
Hydrography
The territory of Ukraine is washed by the waters of the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. Almost all rivers belong to the basins of those seas up to 90%. Much less rivers belong to the Baltic Sea basin. There are seven major rivers in Ukraine: Desna, Dnipro, Dnister, Danube, Prypiat, Siverian Donets, and Southern Buh.
Climate
See also: Climate of Ukraine
Ukraine has a temperate continental climate; Mediterranean only on the southern Crimean coast. Precipitation in Ukraine is disproportionately distributed, highest in west and north and less in east and southeast. Winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland; summers are warm across the greater part of the country, very hot in the south.
Natural resources
Significant natural resources in Ukraine include: iron ore, coal, manganese, natural gas, oil, salt, sulfur, graphite, titanium, magnesium, kaolin, nickel, mercury, timber, arable land.
Environmental issues
Inadequate supplies of potable water; air and water pollution; deforestation; radiation contamination in the northeast from 1986 accident at Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant.
See also
References
- CIA World Factbook, Entry for Ukraine updated May 15 2008.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||